DEFINITION:

A computer network is a group of devices connected with each other through a transmission medium such as wires, cables etc. These devices can be computers, printers, scanners, Fax machines etc. The purpose of having computer network is to send and receive data stored in other devices over the network.![]()

The purpose of having computer network is to send and receive data stored in other devices over the network. These devices are often referred as nodes. There are FIVE BASIC COMPONENTS of a computer network:

Message: It is the data or information which needs to be transferred from one device to another device over a computer network.
Sender: Sender is the device that has the data and needs to send the data to other device connected to the network.
Receiver: A receiver is the device which is expecting the data from other device on the network.
Transmission media: In order to transfer data from one device to another device we need a transmission media such as wires, cables, radio waves etc.
Features of a Computer Network
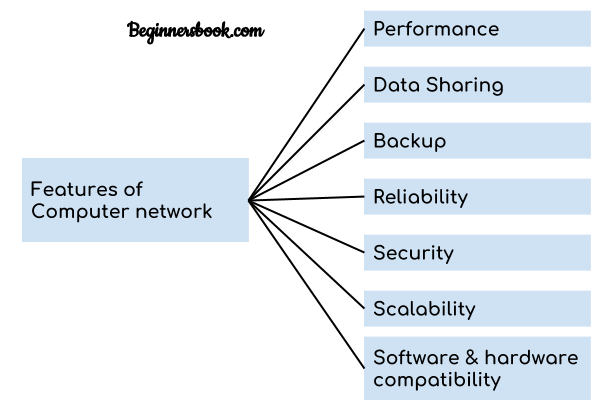
A computer network has following features:
Performance: Performance of a computer network is measured in terms of response time. The response time of sending and receiving data from one node (computer in a computer network are often referred as node) to another should be minimal.
Data Sharing: One of the reason why we use a computer network is to share the data between different systems connected with each other through a transmission media.
Backup: A computer network must have a central server that keeps the backup of all the data that is to be shared over a network so that in case of a failure it should be able to recover the data faster.
Software and hardware compatibility: A computer network must not limit all the computers in a computer network to use same software and hardware, instead it should allow the better compatibility between the different software and hardware configuration.
Security: A computer network should be secure so that the data transmitting over a network should be safe from unauthorised access. Also, the sent data should be received as it is at the receiving node, which means there should not be any loss of data during transmission.
Scalability: A computer network should be scalable which means it should always allow to add new computers (or nodes) to the already existing computer network.

Different types of networks
Different types of (private) networks are distinguished based on their size (in terms of the number of machines), their data transfer speed, and their reach. Private networks are networks that belong to a single organisation. There are usually said to be three categories of networks:

- LAN (local area network)
- MAN (metropolitan area network)
- WAN (wide area network)
There are two other types of networks: TANs (Tiny Area Network), which are the same as LANs but smaller (2 to 3 machines), and CANs (Campus Area Networks), which are the same as MANs (with bandwidth limited between each of the network’s LANs).
LAN
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It’s a group of computers which all belong to the same organisation, and which are linked within a small geographic area using a network, and often the same technology . A local area network is a network in its simplest form. Data transfer speeds over a local area network can reach up to 10 Mbps (such as for an Ethernet network) and 1 Gbps (as with FDDI or Gigabit Ethernet). A local area network can reach as many as 100, or even 1000, users. By expanding the definition of a LAN to the services that it provides, two different operating modes can be defined.
MANs
MANs (Metropolitan Area Networks) connect multiple geographically nearby LANs to one another (over an area of up to a few dozen kilometres) at high speeds. Thus, a MAN lets two remote nodes communicate as if they were part of the same local area network. A MAN is made from switches or routers connected to one another with high-speed links (usually fibre optic cables).
WANs
A WAN (Wide Area Network or extended network) connects multiple LANs to one another over great geographic distances. The speed available on a WAN varies depending on the cost of the connections (which increases with distance) and may be low. WANs operate using routers, which can “choose” the most appropriate path for data to take to reach a network node. The most well-known WAN is the Internet.
NETWORK PROTOCOLS:

Networking Models
There are two theoretical models used to describe the way networking should work.
- OSI Model
- TCP/IP Model
It covers the following topics –

- History
- Layered Network Model
- Layering Concepts and Benefits
- TCP or IP Protocol Architecture
- RFC
- Application Transport Internet and Network Access Layer
- Devices at different layers
- Data Encapsulation
- The OSI Reference Model
- OSI Layers and Their Functions
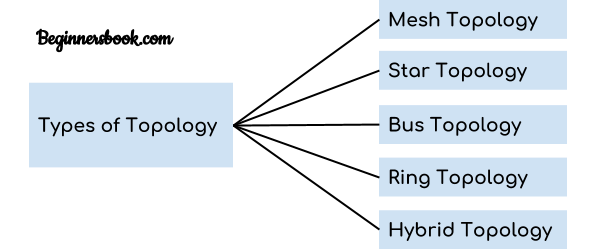
NETWORK TOPOLOGY:

There are five types of topology in computer networks:
1. Mesh Topology
2. Star Topology
3. Bus Topology
4. Ring Topology
NETWORK ARCHITECTURE:
A Computer Architecture is a design in which all computers in a computer network are organized. A architecture defines how the computers should get connected to get the maximum advantages of a computer network such as better response time, security, scalability etc. The two most popular computer architectures are P2P (Peer to Peer) and Client-Server architecture.

SOURCE:
LINK: https://beginnersbook.com/2019/03/introduction-to-computer-network/
FOLLOW US: https://instagram.com/tech.rangers?igshid=1pdqff2ogi9lb
